”Mental toughness is a state of mind – you could call it character in action.”
Vince Lombardi
”Mental Toughness is doing the right thing for the team when it`s not the best thing for you. ”
Bill Belichick
”I’ve missed more than 9000 shots In my career. I’ve lost almost 300 games. 26 times, I’ve been trusted to take the winning shot and missed. I’ve failed over and over and over again in my life. And that is why I succeed.”
Michael Jordan
Succeeding in sports is a long and complex process. The journey to the top involves a number of challenges and turning points that will ultimately determine success. When researching successful athletes, they are often described as determined, committed, disciplined and people who have accepted the challenge and the journey with gratitude. But most of all, they are all united by a mentally hard mindset that believes that dreams can be achieved through patience and acceptance of challenges.
Gucciardi and Hanton (2016) describe mental toughness as a personal capacity to deliver consistently high levels of performance despite varying levels of obstacles and challenges, distractions, pressures, and adversity. It can also be seen in the ability to maintain focus and cope with stress. In successful sports stories, it is often accompanied by resilience and ability to rise from challenges to victory. Clough, Earle and Sewell (2002) divide mental toughness into four dimension (The 4Cs):
Mental toughness in training and competition
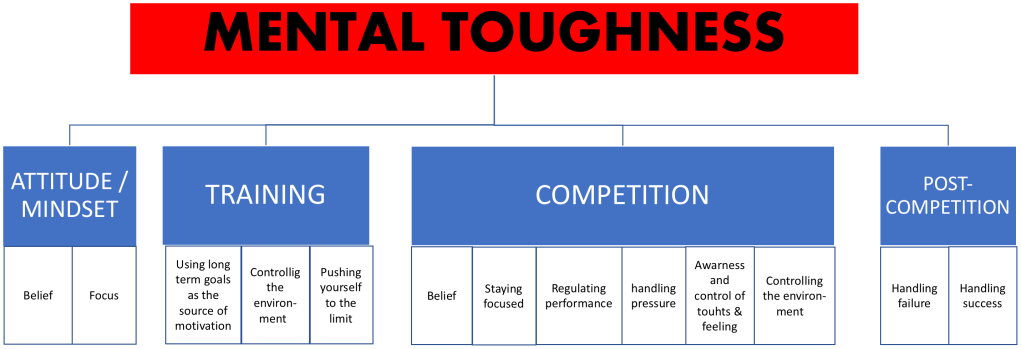
The right attitude and mindset for the athlete is everything. An athlete must have a strong belief in himself and his goals. This is especially emphasized in difficult times. Indeed, mental toughness is often measured the most when things are not going as planned. Succeeding in sports is a long-term process, which is why belief in one’s own success is a key factor. Successes along the way help the athlete to continue and strengthen their faith. Often, however, belief alone is not enough, a clear reason for doing sport and a goal is needed. This makes it easier to stay focused and prioritize things. A clear vision of the goal will help the athlete stay focused and make everyday choices which support his or her goal setting in the short and long term.
Strong belief and clear focus, helps the athlete to train with a purpose. Goals provide extra motivation and help the athlete drive themselves to the limit. As the goal of training is development, this requires control of the environment.Mentally tough athletes shape their own environment and take responsibility for their own actions, which increases their sense of control. When the training is done with the quality and the environment supports the development, it is more likely to succeed in the competition. Mentally tough athletes are able to deal with factors related to the competitive situation, such as uncertainty and stress, and are at the their best level when it matters the most. They are able to adapt to the circumstances, control their own feelings and thoughts, and are able to perform even in challenging situations. Post-performance self-reflection is an important part of mental toughness. It is important to learn to deal with emotions after performance, whether it is a success or a failure. When analyzing performance, it is important to consider the factors that led to the outcome. Each performance teaches something and analyzing them helps to set a goal and maintain focus.
Psychological flexibility and resilience
Psychological flexibility is a skill or set of small skills that allows one to perceive the thoughts and feelings produced by one’s mind and to detach oneself from their power. In addition, psychological flexibility is the ability to act according to one’s own values in different situations despite possible unpleasant thoughts, feelings, and feelings within the body. In sports, it is impossible to control all events, but our own reaction to them can always be controlled. We decide how we react and what happens next. In practice, this means that we must first become aware of our own feelings and thoughts. Then take a distance from them and finally act according to our own values. Naturally, failures cause strong feelings in us but they should never control too much what we do.
In sport, the goal is to reach maximum potential, which is why it is a learning process that also includes failures. Resilience is an athlete’s ability to recover mentally, which is accentuated especially when faced with failures. It is a capacity or skill that helps an athlete to function successfully or adapt after a major set back or unpleasant life event. Resilience can be seen as a characteristic that some have and others do not. It can also be seen as a dynamic process where development can take place. In short, it is a quality that helps an athlete to cope with change and helps them function in a changing sports world. Psychological resilience consists of six components (Hayes, Luoma, Bond, Masuda & Lillis 2006) , which are values, commitment to living according to values, living in the present moment, perceptive self, acceptance, and impaired mental control.
Mental toughness in sport
Source:
Clough, P., Earle, K. & Sewell, D. 2002. Mental toughness: The concept and its measurement. Solutions in sport psychology.
Guggiardi, D. & Hanton, S. 2016. Mental toughness: Critical reflections and future considerations. The routledge international handbook of sport psychology. New York, Routledge.
Hayes, S.C., Luoma, J.B., Bond, F.W., Masuda, A. & Lillis, J. 2006. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy: Model, processes and outcomes. Behaviour Research and Therapy.
Jones, G., Hanton, S. & Connaughton, D. 2007. A framework of mental toughness in the world’s best performers. The Sport Psychologist.
Tossavainen, A. & Peltonen. A. 2021 Psyykkinen valmennus. Fitra.


Published by